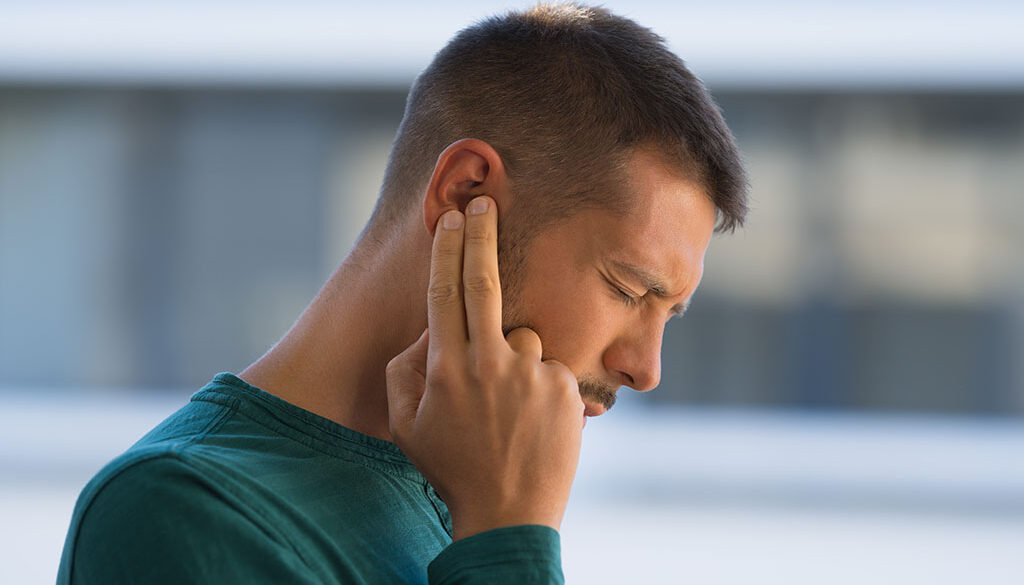
It is usual to occasionally hear an odd sound in the ears, such as ringing, popping, hissing, or buzzing. Everyone has sometimes experienced these strange sounds in their ears. It’s common to compare ear crackling to the sound a bowl of Corn Flakes makes after adding milk. It may be a sign of typical seasonal allergies. Crackling in ear might also be a precursor to a more severe issue.
Your ears may crackle due to several causes, and it typically does not indicate anything dangerous. However, if it happens frequently, it might be a sign of a serious issue and may impact a person’s quality of life.
Keep reading for more details on the causes and treatments of ringing in the ears.
What causes ear crackling and how to find relief
Do you experience a mysterious crackling sound in ear when swallowing, such as thumping, buzzing, or ringing? If you’re wearing hearing aids and this is happening, you might need to visit our office for an adjustment. If you don’t use hearing aids, however, those sounds are probably coming from inside your ears.
You shouldn’t get frightened because of this. Contrary to appearances, your ears are much more complicated on the inside. Most of these sounds are short and harmless, but you must schedule counselling with the doctor if they are painful or persistent.
Causes of Crackling in Ears
Your ears are a complicated subject. They convert sound waves into information your brain can understand using several tiny muscles, bones, and nerves. You may experience buzzing in your ears as a result for a variety of reasons.
Here are some of the most frequent causes of crackling sounds.
Earwax:
Earwax is the most simple cause of crackling popping in ear. When you move your jaw, excessive earwax blockage in your inner ear may cause “cracking” sounds. This might occur naturally. Additionally, using cotton buds to clean your ears can result in it. Earwax shields the ear canal, which keeps it clean and healthy. To avoid excessive buildup, earwax typically clears itself. Disruption of the clearing, however, can result in the accumulation of too much wax, which can lead to tinnitus or hearing loss.
Clogged eustachian tubes:
The Eustachian tube, also called the auditory canal, runs from the edge of your upper throat to the middle ear in each of your ears. The eustachian tube aids in infection prevention, safeguards your ears from loud noises, and stabilises the pressure inside your ears.
The tube usually remains closed when you ingest, yawn, or chew. This motion maintains the pressure. However, you might hear popping or buzzing sounds if it does not open and shut as it should or if external pressure puts more strain on the tube. It could also affect your hearing.
Middle ear infections:
“Acute otitis media” is another name for a middle ear infection. Although middle ear infections can affect anyone at any age, a middle ear infection is typically more frequent in children between the ages of 6 and 24 months than in adults. When y Your eustachian tubes become blocked and unable to drain fluid, it occurs. That liquid may gather and get infected. This causes the ears to make crackling noises.
Prevention:
The ear is a delicate organ. Loud noises, infections, and poor posture can all harm the ear. Because they are simple to ignore, ear problems are frequently left untreated. But it’s time to act if you experience continuous ear pain, tinnitus, nausea or vomiting, vertigo, hearing loss, and other clinical signs of an ear disorder.
You can use first aid techniques or DIY remedies such as chewing, swallowing, yawning, TMJ exercises, over-the-counter products, earwax irrigation, etc. It’s time to see an ear specialist or audiologist if the crackling in the ear continues to be persistent and won’t stop on its own.
Also read: What Happens If You Put Alcohol in Your Ear?
Crackling ear prevention tips
Try the following preventative measures to avoid popping or crackling ears:
- Stay healthy; consume five fruits and vegetables daily, exercise frequently, wash your hands regularly, and avoid sick people.
- Quit smoking. Smoking can cause or aggravate ETD, so give up the habit immediately.
- Avoid allergens: To reduce ETD, avoid your triggers if you are prone to seasonal allergies. Reduce your time in noisy environments by wearing ear protection.
- Don’t use cotton swabs: This may force earwax further in your ear canal.
- Avoid environmental irritants: Try to stay far from environmental irritants. Pollution, secondhand smoke, and allergens could all be factors in eustachian tube dysfunction.
- Avoid loud noises. Exposure to loud noises can harm your ears and worsen conditions like tinnitus. To avoid causing ear damage, buy high-quality ear protection if you’re going to a concert or working in a noisy environment.
Treatment for crackling in the ear:
Crackling in the ears doesn’t always require medical attention, primarily if it only occasionally occurs. The cause of your ear crackling will determine how to treat it. Some of the treatment options are:
Treatment for earwax buildup:
Home remedies for earwax blockage include irrigation equipment to gently wash the softened wax and over-the-counter (OTC) wax soothing drops. These treatments, however, are only appropriate for those with healthy eardrums. You can learn how to safely utilize drops and irrigation tools from a doctor or pharmacist. A doctor can also assist in clearing earwax buildup.
Treatment for ETD
Depending on the underlying cause, ETD may require different treatments. Some causes, like a light cold or descending from an altitude, may be mild or infrequent and not call for any medical interventions. Other reasons, like GERD and cystic fibrosis, might need medical attention.
Treatment for ear infection
The immune system may cure a minor ear infection. Treatment options like over-the-counter painkillers can help reduce discomfort. Clinical care is necessary for infections that last longer than two to three days. For bacterial infections, doctors may recommend antibiotics.
Final words
You might occasionally hear popping or crackling in ear. Numerous conditions, including acute otitis media, eustachian tube dysfunction, and earwax buildup, can result in ear crackling. If you don’t also have an earache or a fever, ear crackling is typically not dangerous. You can try several home remedies to help stop the noise in your ears. However, plan an appointment with your doctor if self-care strategies fail or your symptoms are severe or persistent.
Medical Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes only and does not constitute medical advice. If you are experiencing symptoms, please consult a healthcare professional.