Spinal stenosis can lead to severe back pain and reduced mobility. If left untreated, it can become a serious condition that results in permanent damage to the spine. Both men and women can experience spinal stenosis, particularly as they age or due to underlying spinal conditions.
In this article, we’ll cover what spinal stenosis is, its symptoms, what causes it, and the most effective modern treatments available. Don’t let spinal stenosis limit your life—learn what steps you can take today.
What Is Spinal Stenosis?
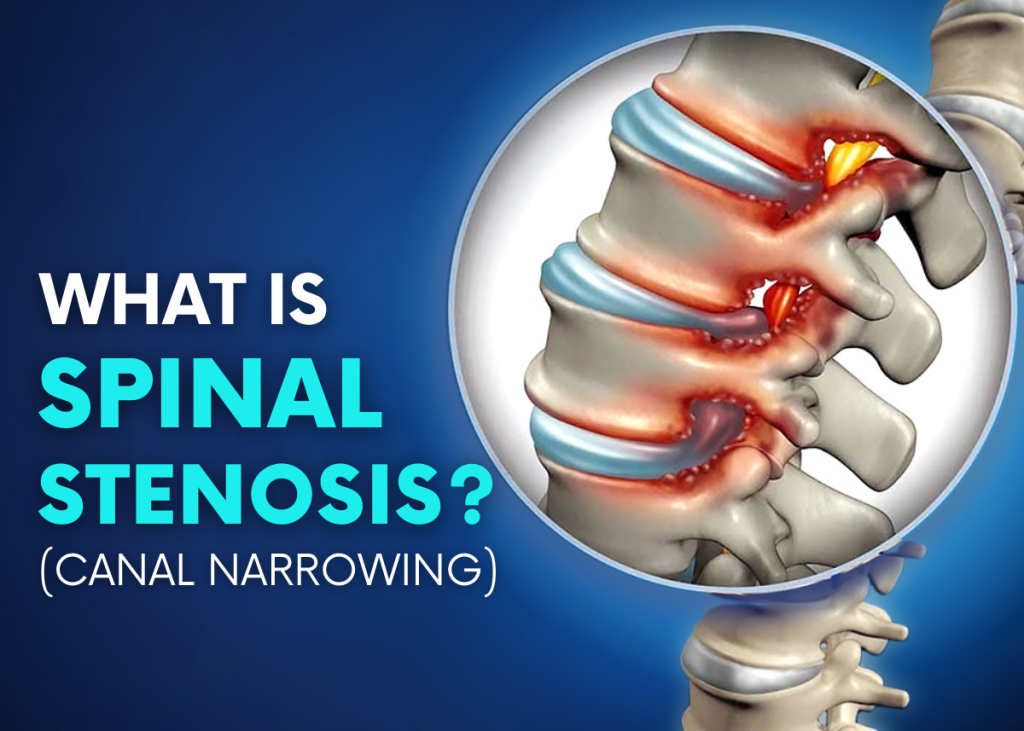
Spinal stenosis is a condition in which the space inside the spinal canal narrows, placing pressure on the spinal cord and the surrounding nerves. It commonly affects the lower back (lumbar spine) and neck (cervical spine) and can lead to a range of discomforting symptoms.
What Causes Spinal Stenosis?
While aging and arthritis are the most common causes, several other conditions can lead to spinal stenosis. Let’s explore the major causes:
1. Bone Spurs
Often due to arthritis or Paget’s disease, bone spurs are bony overgrowths that press against the spinal canal, causing pain and nerve compression.
2. Congenital Small Spinal Canal
Some individuals are born with a naturally small spinal canal, increasing the risk of nerve compression and related symptoms.
3. Herniated Discs
Discs act as cushions between the vertebrae. Over time, they may dry out or slip out of place, irritating nearby nerves or the spinal cord itself.
4. Spinal Injuries
Trauma from accidents can displace vertebrae or cause fractures, leading to narrowing of the spinal canal and subsequent stenosis.
5. Post-Surgical Swelling
Swelling after back surgery can cause temporary or lasting pressure on the spinal cord or nerves.
6. Enlarged Ligaments
With age, spinal ligaments can thicken and stiffen, pressing into the spinal canal and contributing to narrowing.
7. Spinal Tumors (Rare)
In rare cases, tumors may form within the spinal canal, compressing nerves and spinal structures.
What Are the Symptoms of Spinal Stenosis?
Not everyone with spinal stenosis experiences symptoms, but when they do occur, they can significantly impact daily life. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent lower back pain
- Neck pain and stiffness
- Leg cramping, especially after standing or walking for long periods
- Numbness, tingling, or weakness in the hands, arms, legs, or feet
- Bladder or bowel control issues (in severe cases)
These symptoms often worsen over time if not properly managed or treated.
Effective Treatments for Spinal Stenosis
Spinal stenosis treatment varies depending on the severity of the condition and the individual’s overall health. Here are the most common and effective approaches:
Strength & Mobility Exercises
Regular exercises can help relieve pressure, improve flexibility, and enhance spinal support. These include:
- Pelvic Tilts: Strengthen core muscles and support spinal alignment.
- Bridges: Target the glutes to reduce strain on the lower back.
- Knee-to-Chest Stretches: Loosen tight back muscles and create temporary relief by increasing space in the spinal canal.
Physiotherapy
Physical therapy is often a first-line treatment to manage spinal stenosis without surgery.
- Increases range of motion and flexibility
- Strengthens core and back muscles
- Includes additional methods like massage, electrostimulation, heat, and cold therapy
Your physiotherapist can develop a personalized plan to reduce pain and inflammation.
Medication
Depending on pain severity, doctors may recommend:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers (like acetaminophen or ibuprofen)
- Prescription medication for nerve pain or inflammation
- Muscle relaxants to reduce spasms
Always consult your healthcare provider before starting or changing any medication.
Surgical Options for Severe Cases
If non-surgical treatments fail after 6 months or more, surgery may be necessary to relieve pressure and stabilize the spine.
Spinal Decompression Surgery
This involves removing parts of the vertebrae pressing on the nerves, such as through a laminectomy, where part or all of the lamina (the back part of the vertebra) is removed.
Spinal Fusion Surgery
Often performed after decompression, spinal fusion involves joining two or more vertebrae using bone grafts, screws, and rods to stabilize the spine. However, it may reduce flexibility and lead to degeneration in surrounding vertebrae.
TOPS™ System (Total Posterior Solution)
An innovative, non-fusion implant that maintains spinal mobility while relieving nerve pressure. It’s a modern alternative for eligible patients looking to avoid fusion-related limitations.
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical attention if your symptoms worsen or persist despite rest or therapy, or if you experience numbness, bladder or bowel issues, or significant weakness. Additionally, if pain or discomfort begins to interfere with your daily activities, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent further complications and reduce the risk of permanent nerve damage.
Conclusion
Spinal stenosis can be a painful and debilitating condition, but you don’t have to live in discomfort. By understanding its causes and symptoms, and by exploring a range of modern treatment options—from exercises to surgery—you can take proactive steps toward relief and recovery.
Whether you’re just beginning to notice symptoms or have been managing spinal pain for years, consult your doctor to find the treatment path that’s right for you. With the right approach, a pain-free and active life is within reach.
Disclaimer: The content on Wellness Derive is for informational purposes only and not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always consult a healthcare provider for medical concerns.